Understanding Credit When Shopping For a Mortgage
This article will cover understanding credit when shopping for a mortgage. Credit and Income are the two most important factors lenders will thoroughly analyze prior to granting credit to borrowers.
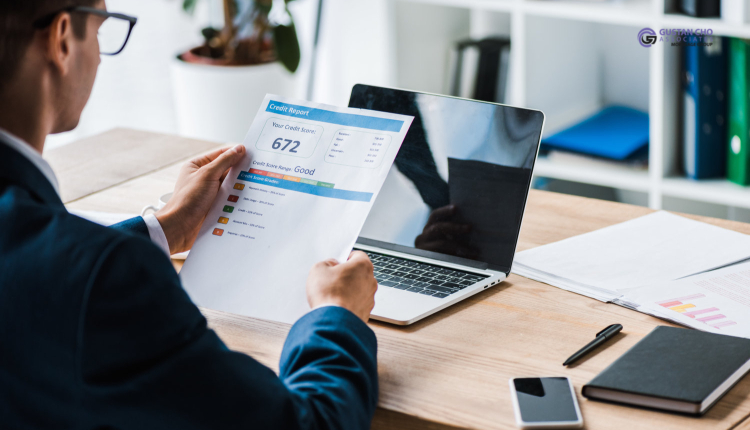
Most borrowers believe that as long as they meet the minimum credit score requirements to qualify for a home loan that they are safe and have nothing to worry about. This is not always the case. It is very important to understanding credit and the importance of the overall credit profile of a borrower. Not just the borrower’s credit scores.
Lenders mainly price mortgage rates on credit scores. Having a lower credit score can cost you tens of thousands of dollars in mortgage interest expenses over the term of your mortgage loan. It is best to try to maximize your credit scores before applying for a mortgage. In the following paragraphs, we will cover understanding credit when shopping for a mortgage loan.
Key Points In Understanding Credit When Shopping For a Mortgage
Here are some key points in understanding credit for borrowers who plan on applying for a home loan.
Borrowers should understand that they have three credit scores. The middle credit score is used by lenders in determining which credit score is the qualifying credit score for a mortgage.. Credit Reports do contain errors.
Consumers should periodically check their credit reports to make sure that all information being reported on their credit reports are accurate. Maxed-out credit cards will definitely lower credit scores.
Importance of Credit When Applying For Mortgage
Borrowers should pay down all of their credit card balances months before applying for a mortgage. This is so they can get the highest possible credit scores. Higher credit scores mean lower mortgage rates.
Lower mortgage rates translate into tens of thousands of dollars of savings over the term of the mortgage loan. Late payments in the past 12 months are considered serious. May be reasons for disqualification for a mortgage. Cannot have credit disputes on charge off accounts. Non-medical collection accounts that have aggregate unpaid outstanding balances of over $1,000 needs credit disputes retracted.
Late payments after bankruptcy, deeds in lieu of foreclosure, foreclosure, and a short sale may be reasons for not being able to qualify for home loans. Borrowers with prior foreclosure or deed in lieu reported on the credit report, lenders go off the recorded date of housing event as the waiting period start date to qualify for FHA, VA, USDA, FANNIE/FREDDIE Mortgages.
How Are Credit Scores Issued
There are three giant credit reporting agencies that issue credit scores. Here are the three major credit bureaus who are in charge of issuing credit scores to borrowers:
- TransUnion
- Equifax
- Experian
Credit Scores Used By Lenders For Qualifying Borrowers
Of the three credit scores, all lenders will use the middle credit score of the borrowers to process the mortgage loan. Here is a loan scenario on how lenders use the middle credit score in qualifying borrowers. For example:
- If a client has credit scores of 620, 650 and 700
- Lenders will use the middle score of 650
The middle score must be at least 620 for most loan programs and lenders:
- Credit scores fluctuate
- Many lenders will have a tool called FICO Analyzer
- FICO Simulator will render potential credit score improvements of borrowers tri-merger credit reports and credit scores
It will state the number of FICO points consumers can increase their credit scores by paying down certain credit tradelines or paying off a collection/charge-off account. Credit Scores average of borrowers and co-borrowers on conventional loans.
Fannie Mae came out with new credit score guidelines. Borrowers with co-borrowers including non-occupant co-borrowers can now average the middle credit scores and the average will be the qualifying credit score. For example, if the borrower has a 700 credit score and the co-borrower has a 600 FICO, Fannie Mae now allows the two middle credit scores to get averaged. The resulting credit score is 650. The minimum credit score to qualify for conventional loans is 620 FICO.
This enables borrowers who otherwise would not qualify for a conventional loan to now qualify. Rates will be priced on the lower middle credit score borrower.
What Is A Credit Score Analyzer?
Many loan officers use a tool called the FICO Analyzer where it will get you a step by step re-scoring instructions on what a borrower needs to do to maximize his or her credit scores. The FICO Analyzer will give you the following results:
- It will give you a potential credit score improvement by paying down certain revolving credit accounts
- It will give you a potential credit score improvement by removing certain credit tradelines
- Examples include removing authorized credit card user accounts
- Especially for authorized credit card revolving tradelines with maxed-out credit balances or a history of late payments
- It will give potential credit score improvements by paying off judgments, tax liens, collections, charge off accounts
It will give potential credit score improvements if paying off certain installment debts.
Understanding Credit and Credit Reports
Understanding Credit, Credit Scores, and being able to read credit reports is not as difficult as it may seem. The first lesson to understanding credit is to realize credit report is made up of four different parts. Credit reports are divided into four sections and the combination of these four parts is what makes up your credit scores:
- Identifying information, credit history, public records, and inquiries
- Identifying information is just that – information that relates to identifying the customer
Be sure to look at this information closely for accuracy such as the following:
- wrong social security numbers
- misspelling of first, middle, or last names
- wrong date of birth
- wrong information of address
Credit History:
- The credit history section is where you will see the individual credit tradelines
This part of the credit report will also not the type of credit established such as installment or revolving accounts:
- whether it is an active credit revolving or installment account or closed accounts
We Will also see the date of the last activity and the high credit limits and your current balance:
- There will also be comments such as the account in credit dispute, account in collections, account charged off
- We Will also see the high credit limit and balance on the account
- May also see comments like collections, charge‐off, or account in default
- Below this section, consumers will also see a section that will report public records such as judgments, tax liens, bankruptcies, foreclosures, short sales, or other public records
- The final section on the credit report is inquiries
- Credit inquiries are done when consumers give creditor and/or employer permission to have access
- It is normally done when applying for new credit or a new job
- Anytime anyone accesses a credit report, an inquiry is generated
Understanding Credit Inquiries
Credit Inquiries is when consumers apply for new credit:
- Consumers are giving the creditor permission to run credit
- Either from one or all of the three credit reporting agencies
- Creditors will then analyze credit scores, payment history, and overall credit report
- They then decide whether or not they will grant credit
- Credit Inquiries will reflect on the credit report
- Whenever consumers apply for a mortgage, the lender will want a letter of explanation on all of the recent credit inquiries on a credit report
- The way you write a letter of explanation for each credit inquiry on the credit report is very simple
A one-line explanation like:
- ” I applied for a credit card to get a lower interest rate credit card”
- That one statement alone should be sufficient
- Consumers will also be asked whether or not credit by the creditor was granted
- Or not and just state whether you were approved or not
Credit Inquiries are divided into two sections:
- “Hard” inquiries are ones the consumer generates when they fill out a credit application
- Will lower a consumer’s credit scores
- When you apply for credit cards, auto loans, and mortgage loans, those are considered hard credit inquiries
- “Soft” inquiries are credit pulls from companies that want to send promotional information, or current creditors monitoring their accounts
- Soft inquiries only show on credit reports given to consumers
Understanding Hard Credit Inquiries
Hard credit inquiries will have a negative impact on your credit scores when you first apply for a particular credit. For example:
- if you apply for a mortgage loan for the very first time
- the first mortgage company that will do a credit pull on credit
- this will definitely have a negative impact on FICO credit scores
It may drop 5 or more FICO points:
- if you apply to multiple lenders within a 30 days time frame, most of the mortgage credit inquiries after the third hard credit pull will have no impact on credit scores
- Same with credit cards as well as auto loans
- The first few hard credit inquiries will have a negative impact on credit scores
- However, after the third hard credit inquiry, it should not affect credit scores too much
Can have 30 plus hard mortgage credit inquiries in a 14 day period and FICO will only count it as one hard credit pull credit inquiry.